Living with peripheral neuropathy can be a daily challenge. The persistent tingling, numbness, or pain can make simple activities feel overwhelming. You’re not alone in this struggle, and like many others, you may be searching for ways to ease your symptoms and reclaim some comfort in your life. Could compression socks for peripheral neuropathy be part of the solution? Let’s explore whether they’re a good choice for managing peripheral neuropathy and how they might help you feel better.
Table of Contents

Understanding Peripheral Neuropathy
What Is Peripheral Neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy refers to damage to the nerves outside your brain and spinal cord. These nerves are responsible for sending signals to and from your brain, so when they’re damaged, it can lead to a range of uncomfortable symptoms. Causes of this condition include:
- Diabetes (one of the most common culprits).
- Physical injuries or trauma.
- Infections and autoimmune diseases.
- Certain medications or toxins.
Common Symptoms
If you’re dealing with peripheral neuropathy, you’ve likely experienced symptoms like:
- A persistent tingling or burning sensation in your hands or feet.
- Numbness or weakness in affected areas.
- Heightened sensitivity to touch.
- Difficulty balancing or walking.
How Peripheral Neuropathy Impacts Daily Life
Peripheral neuropathy doesn’t just affect your body; it impacts your quality of life. Pain and discomfort can make everyday activities—like walking, exercising, or even resting—challenging. This condition might also leave you feeling frustrated or drained as you search for effective ways to manage your symptoms.
What Are Compression Socks?
How Do They Work?
Compression socks are specialized garments designed to gently squeeze your legs, improving blood flow and reducing swelling. The pressure they apply is often graduated, meaning it’s tightest around your ankle and gradually loosens as it moves up your leg. This promotes circulation and can help alleviate some of the discomfort caused by poor blood flow.
Types of Compression Socks
When shopping for compression socks, you’ll come across different styles and pressure levels:
- Knee-high socks: Cover the lower leg, commonly used for mild symptoms.
- Thigh-high socks: Provide extended coverage for more significant circulation issues.
- Full-length compression stockings: Often recommended for more severe cases.
- Pressure levels: Range from mild (15-20 mmHg) to firm (30-40 mmHg). Always consult your doctor to find the right level for your needs.
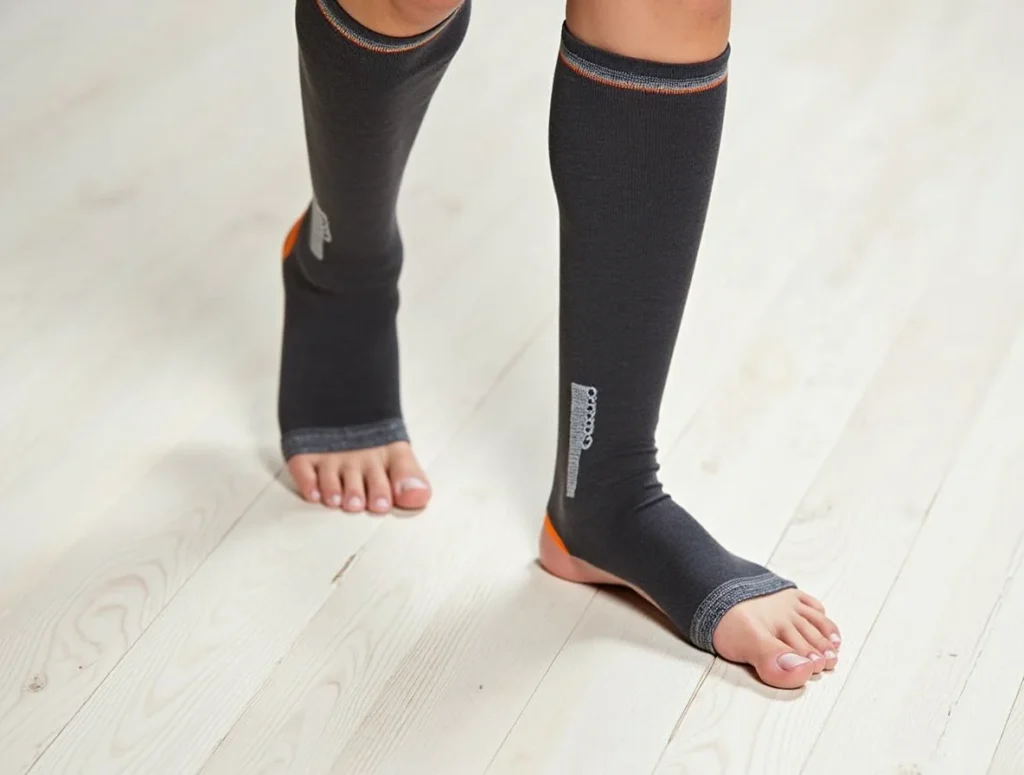




Are Compression Socks Good for Peripheral Neuropathy?
Benefits of Compression Socks for Neuropathy
Compression socks can offer several potential benefits for those dealing with peripheral neuropathy:
- Improved circulation: By enhancing blood flow, these socks can help deliver oxygen and nutrients to your nerves, which might alleviate some discomfort.
- Reduced swelling: Consistent pressure can minimize fluid buildup in your legs and feet, reducing puffiness and pain.
- Pain relief: The gentle compression may ease some of the burning or tingling sensations you’re experiencing.
Limitations and Precautions
While compression socks can be helpful, they’re not suitable for everyone. If you have severe arterial disease or certain skin conditions, wearing them could do more harm than good. In fact, improper use of compression socks can cause additional damage, such as restricted blood flow or skin irritation. Always consult your healthcare provider before trying compression socks to ensure they’re safe for your specific condition.
How to Choose the Right Compression Socks for Peripheral Neuropathy
Key Factors to Consider
When selecting compression socks, keep these factors in mind:
- Pressure level: Mild compression (15-20 mmHg) is often ideal for managing peripheral neuropathy. For more severe symptoms, moderate compression (20-30 mmHg) might be recommended.
- Material: Look for breathable, moisture-wicking fabrics like nylon or spandex to keep your feet comfortable throughout the day.
- Fit: Proper sizing is crucial. Socks that are too tight can worsen your symptoms, while loose socks won’t provide the desired benefits.
Recommended Brands and Types
To simplify your search, here’s a quick comparison of popular compression sock brands:
| Brand | Compression Level | Material | Price Range | Customer Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A | Mild (15-20 mmHg) | Cotton blend | $20-$30 | 4.5/5 |
| Brand B | Moderate (20-30 mmHg) | Nylon/spandex | $25-$40 | 4.7/5 |
| Brand C | Firm (30-40 mmHg) | Polyester blend | $30-$50 | 4.6/5 |
How to Use Compression Socks Safely and Effectively
Tips for Best Results
To get the most out of your compression socks:
- Wear them during the day: Put them on in the morning and remove them before bedtime.
- Check the fit regularly: Make sure they’re snug but not cutting off circulation.
- Maintain cleanliness: Wash your socks after each use to maintain their elasticity and prevent skin irritation.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid these pitfalls to ensure your compression socks work as intended:
- Skipping a proper fit: Ill-fitting socks can lead to discomfort or worsen symptoms.
- Wearing them without medical advice: Always consult a doctor, especially if you have other health conditions.
- Overusing compression socks: Prolonged use without breaks can sometimes lead to skin damage or decreased circulation.

Other Ways to Manage Peripheral Neuropathy
Complementary Treatments
While compression socks may provide relief, they’re most effective when combined with other strategies:
- Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise and a healthy diet can support nerve health.
- Medications: Pain relievers and nerve-specific treatments may be prescribed.
- Supplements: Vitamins like B12 are essential for maintaining nerve function.
Recipes for a Neuropathy-Friendly Diet
Your diet plays a critical role in managing inflammation and supporting overall health. Try this anti-inflammatory recipe:
| Recipe | Ingredients |
|---|---|
| Smoothie Bowl | Spinach, blueberries, almond milk, chia seeds |
| Anti-inflammatory Salad | Kale, walnuts, olive oil, turmeric dressing |
These nutrient-packed meals can help reduce inflammation and provide your body with the nutrients it needs to heal.
FAQ Section
Can Compression Socks Cure Peripheral Neuropathy?
Compression socks cannot cure peripheral neuropathy. Peripheral neuropathy occurs due to damage to the peripheral nerves, which compression socks cannot reverse. However, they may help manage some symptoms by improving blood flow, reducing swelling, and alleviating discomfort.
If you’re exploring treatment options for peripheral neuropathy, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to address the underlying cause of your condition and determine the most effective treatment plan.
How Long Should I Wear Compression Socks?
The duration for wearing compression socks depends on your specific condition and your doctor’s recommendations. However, general guidelines include:
- Daytime Use: Most people benefit from wearing compression socks during the day, especially when they are active or on their feet. Put them on in the morning and remove them before going to bed.
- Post-Surgical or Medical Use: If prescribed for a medical condition or recovery, follow your doctor’s instructions carefully, which may include wearing them for longer durations.
- Short Breaks: Avoid wearing compression socks 24/7 unless explicitly advised by your doctor. Giving your legs a break at night allows your skin to breathe and helps prevent irritation.
Always ensure the socks fit properly and monitor for any discomfort, skin changes, or restricted circulation. If you experience any issues, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Are Compression Socks Safe for Everyone?
Compression socks are generally safe for many people, but they are not suitable for everyone. Specific health conditions or improper use can make them unsafe. Here’s what to consider:
When Compression Socks May Be Unsafe:
- Severe Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Compression socks can further restrict blood flow in people with PAD, worsening the condition. - Skin Conditions or Sensitivities
If you have conditions like eczema, dermatitis, or open sores, compression socks may irritate the skin or delay healing. - Diabetic Neuropathy with Poor Circulation
For individuals with severe diabetes-related neuropathy, compression socks may restrict circulation and lead to complications. - Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
While compression socks can prevent DVT, wearing them without medical supervision during an active clot may increase risks. - Allergic Reactions
Sensitivity to materials in the socks (e.g., latex or synthetic fibers) can cause irritation or allergic reactions.
Safety Tips:
- Consult Your Doctor First: Always talk to a healthcare professional, especially if you have chronic conditions, such as diabetes or vascular issues.
- Check Fit and Compression Level: Ill-fitting or overly tight socks can cause more harm than good. Use the recommended compression level (e.g., mild 15-20 mmHg or moderate 20-30 mmHg).
- Monitor Skin and Circulation: Check your legs regularly for redness, swelling, or discomfort.
By following medical advice and proper guidelines, compression socks can be a helpful tool for many, but they should be used cautiously and under supervision when certain health conditions are present.
What’s the Best Compression Level for Neuropathy?
The best compression level for peripheral neuropathy depends on the severity of your symptoms and your medical condition. Generally, mild to moderate compression is recommended, but you should always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice. Here’s a guide to common compression levels:
Recommended Compression Levels
- Mild Compression (15-20 mmHg)
- Ideal for mild symptoms of neuropathy or for general comfort and support.
- Suitable for individuals with slight swelling or mild discomfort.
- Moderate Compression (20-30 mmHg)
- Commonly recommended for managing more noticeable neuropathy symptoms, including moderate swelling or discomfort.
- Often prescribed for people with diabetes or those with circulatory issues related to neuropathy.
- Firm Compression (30-40 mmHg)
- Typically used under medical supervision for severe symptoms or advanced cases where circulation needs significant support.
- May be prescribed for individuals with chronic venous insufficiency or other serious vascular conditions.
Factors to Consider
- Comfort: Compression should feel snug but not restrictive.
- Fit: Poorly fitted socks can worsen neuropathy symptoms.
- Doctor’s Guidance: Your doctor may recommend specific levels based on your overall health and circulation needs.
Using the appropriate compression level can provide relief and improve circulation, but improper use may exacerbate symptoms. Always start with mild or moderate levels unless advised otherwise by a medical professional.
How often should I wear compression socks in neuropathy pain?
The frequency of wearing compression socks for neuropathy pain depends on the cause of your neuropathy, the severity of your symptoms, and the advice of your healthcare provider. Here are some general guidelines:
- Daily Use for Symptom Relief
Many people wear compression stockings daily, especially while doing activities such as walking, working or standing for long periods. This helps improve blood circulation and reduce swelling, relieving pain and discomfort.
Some may benefit from wearing them at specific times of the day, such as in the morning or during activities that worsen symptoms. - Avoid Prolonged or Continuous Wear
While compression socks can be helpful, they should typically not be worn 24/7 unless directed by a healthcare provider. Your legs and skin need time to breathe, especially at night. - Choose the Right Compression Level
Mild Compression (15-20 mmHg): Often recommended for mild neuropathy symptoms or prevention.
Moderate Compression (20-30 mmHg): Used for more pronounced symptoms or moderate swelling.
Higher Compression (30-40 mmHg or above): Only under medical supervision, especially if you have conditions like diabetes or severe circulatory issues. - Specific Recommendations
Diabetic Neuropathy: People with diabetes must be cautious, as too much compression can restrict circulation further. Always consult with a doctor.
Peripheral Neuropathy (Non-Diabetic): Wearing compression socks during activities can improve blood flow and reduce pain or tingling. - Consult Your Doctor
If you experience neuropathy pain, consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice. They can:
Recommend the appropriate compression level.
Suggest the best schedule based on your condition and daily activities.
Rule out contraindications (e.g., severe arterial disease or open wounds).
In summary, compression socks can be worn daily for neuropathy pain, but for limited hours and based on professional guidance. If you notice increased discomfort, numbness, or skin changes, discontinue use and seek medical advice.
Conclusion
Peripheral neuropathy can make life difficult, but tools like compression socks offer a simple, accessible way to manage symptoms and find relief. By improving circulation and reducing swelling, these socks might help you feel more comfortable and confident in your daily activities. However, it’s important to be aware of their potential risks and limitations. Improper use or wearing them without medical advice could lead to additional issues. Always consult with a healthcare provider to ensure you’re making the best choices for your condition. While there’s no cure for neuropathy, small changes like these can have a meaningful impact on your quality of life.
- Spectra Sock for Prosthetic Foot: Comfort, Durability, and Enhanced Mobility
- best Socks for Foot Neuropathy – Shop Comfort and Support
- Do Compression Socks Help Neuropathy? Find the Right Pair Now
- Best Compression Socks for Neuropathy – Relieve Pain Today
- Socks for Neuropathy: How They Help Relieve Foot Pain and Improve Comfort